
- Chinese: Business Department 0539-8782638
- English: chau@dengzhuochem.com

- Chinese: Business Department 0539-8782638
- English: chau@dengzhuochem.com

About Ammonia Production
2023-10-13
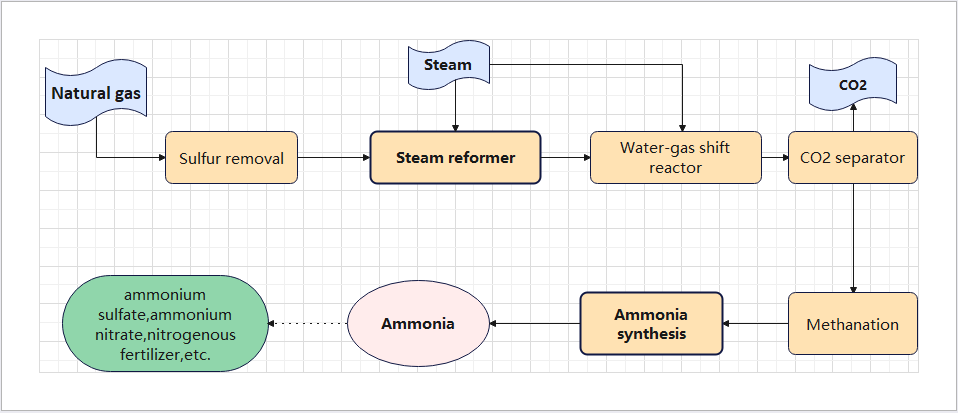
The production of ammonia is relatively simple, and the industrial reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperature and pressure is used to synthesize ammonia. However, in the process of producing hydrogen, a lot of resources such as coal and natural gas are consumed, and a lot of carbon emissions are generated. According to the data of China Gas Industry Association, the total carbon dioxide emissions of China's synthetic ammonia industry in 2020 will be 219 million tons, accounting for 19.9% of the total emissions of the chemical industry. Ammonia is one of the most basic chemical raw materials and is widely used in chemical industry. Ammonia can be used in the production of agricultural fertilizer raw materials (nitrogen fertilizer) such as urea, and can also be used in the production of chemical supplies such as nitric acid. As the most basic and simplest nitrogen-containing raw material in industry, almost all nitrogen-containing compounds are derived from ammonia. Ammonia can also be used as a new green fuel or hydrogen carrier. The use of green ammonia fuels produces virtually no carbon emissions. In addition, ammonia is easy to compress, the volume energy density of liquid ammonia is more than 35% higher than that of liquid hydrogen, and it can decompose and release hydrogen under catalytic conditions, which is an excellent hydrogen energy carrier.
Ammonia production takes place worldwide, mostly in large-scale manufacturing plants that produce 183 million metric tons of ammonia (2021) annually. Leading producers are China (31.9%), Russia (8.7%), India (7.5%), and the United States (7.1%). 80% or more of ammonia is used as fertilizer. Ammonia is also used for the production of plastics, fibers, explosives, nitric acid (via the Ostwald process), and intermediates for dyes and pharmaceuticals.

<< Previous Page
Next Page >>